| Clinical Applications ของ lung scan |
 |
| Pulmonary embolism |
 เป็นภาวะที่เกิดจากการที่มี emboli มาอุดตันในหลอดเลือดของปอด โดยมากมักมีสาเหตุมาจากการที่ผู้ป่วยมีภาวะ deep venous thrombosis อยู่ก่อน การวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism จากการอาการทางคลินิกทำได้ยาก เนื่องจากอาการหอบเหนื่อย เจ็บหน้าอก ไอ อาจพบได้ในโรคอื่นๆ สำหรับการเจาะเลือดตรวจดูระดับ D-dimer และภาพถ่ายเอกซเรย์ปอด (chest x-ray) พบว่าไม่มีความจำเพาะเจาะจง เป็นภาวะที่เกิดจากการที่มี emboli มาอุดตันในหลอดเลือดของปอด โดยมากมักมีสาเหตุมาจากการที่ผู้ป่วยมีภาวะ deep venous thrombosis อยู่ก่อน การวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism จากการอาการทางคลินิกทำได้ยาก เนื่องจากอาการหอบเหนื่อย เจ็บหน้าอก ไอ อาจพบได้ในโรคอื่นๆ สำหรับการเจาะเลือดตรวจดูระดับ D-dimer และภาพถ่ายเอกซเรย์ปอด (chest x-ray) พบว่าไม่มีความจำเพาะเจาะจง |
 ventilation perfusion scintigraphy เป็นวิธีที่มีประโยชน์อย่างมากในการช่วยวินิจฉัยภาวะนี้ เนื่องจากเป็นวิธีที่ noninvasive และ มีความแม่นยำค่อนข้างสูง โดยลักษณะที่ typical ของ lung scan ใน pulmonary embolism จะมีลักษณะที่เรียกว่า segmental ventilation perfusion mismatch defect (รูปที่ 8) กล่าวคือ ใน perfusion scan จะเห็นperfusion defect (คือบริเวณที่ไม่มี activity ของสารเภสัชรังสี) ซึ่งเป็นผลมาจากการที่มี emboli อุดในหลอดเลือดปอด โดย perfusion defects ดังกล่าวมีลักษณะเป็น segment , multiple และ peripheral กล่าวคือ มีลักษณะเป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยม ฐานอยู่ด้านริมนอกของปอด( ตามลักษณะการแตกแขนงของหลอดเลือด) และมักมี defect มากกว่าหรือเท่ากับ 2 defects ขึ้นไป ventilation perfusion scintigraphy เป็นวิธีที่มีประโยชน์อย่างมากในการช่วยวินิจฉัยภาวะนี้ เนื่องจากเป็นวิธีที่ noninvasive และ มีความแม่นยำค่อนข้างสูง โดยลักษณะที่ typical ของ lung scan ใน pulmonary embolism จะมีลักษณะที่เรียกว่า segmental ventilation perfusion mismatch defect (รูปที่ 8) กล่าวคือ ใน perfusion scan จะเห็นperfusion defect (คือบริเวณที่ไม่มี activity ของสารเภสัชรังสี) ซึ่งเป็นผลมาจากการที่มี emboli อุดในหลอดเลือดปอด โดย perfusion defects ดังกล่าวมีลักษณะเป็น segment , multiple และ peripheral กล่าวคือ มีลักษณะเป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยม ฐานอยู่ด้านริมนอกของปอด( ตามลักษณะการแตกแขนงของหลอดเลือด) และมักมี defect มากกว่าหรือเท่ากับ 2 defects ขึ้นไป |
 ส่วนใน ventilation scan จะปกติ (รูป B) ส่วนใน ventilation scan จะปกติ (รูป B) |
 |
| A : Perfusion scan |
|
 |
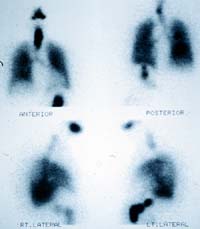 |
| B : Ventilation scan |
|
|
รูปที่ 8 แสดงภาวะ pulmonary embolism และ
Deep veiw thrombosis |
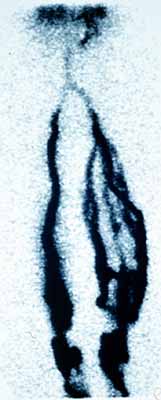 |
C : ภาพ Venogram ของผู้ป่วย
รายเดียวกัน
ที่มีภาวะ
deep venous thrombosis
ของขาข้างซ้าย |
|
|
|
 เนื่องจาก perfusion scan แสดงถึง distribution ของ pulmonary arterial blood flow และ ventilation scan แสดงถึง distribution ของ ventilation ไม่ได้เป็นการแสดงถึงพยาธิสภาพอย่างแท้จริงของภาวะ pulmonary embolism ดังนั้นการแปลผลจึงมักบอกเป็น probability ที่จะเป็น pulmonary embolism มากกว่าที่จะให้การวินิจฉัยลงไป โดย probability จะแบ่งออกเป็น high, intermediate และ low probability เนื่องจาก perfusion scan แสดงถึง distribution ของ pulmonary arterial blood flow และ ventilation scan แสดงถึง distribution ของ ventilation ไม่ได้เป็นการแสดงถึงพยาธิสภาพอย่างแท้จริงของภาวะ pulmonary embolism ดังนั้นการแปลผลจึงมักบอกเป็น probability ที่จะเป็น pulmonary embolism มากกว่าที่จะให้การวินิจฉัยลงไป โดย probability จะแบ่งออกเป็น high, intermediate และ low probability |
 ในการแปลผล lung scan ควรใช้ภาพเอกซเรย์ปอด (chest X-ray) ที่ถ่ายห่างกันไม่เกิน 24 ชั่วโมงร่วมด้วย เพื่อเปรียบเทียบกับบริเวณที่ผิดปกติใน lung scan ในการแปลผล lung scan ควรใช้ภาพเอกซเรย์ปอด (chest X-ray) ที่ถ่ายห่างกันไม่เกิน 24 ชั่วโมงร่วมด้วย เพื่อเปรียบเทียบกับบริเวณที่ผิดปกติใน lung scan |
 ในปัจจุบันหลายสถาบันนิยมใช้ criteria ของ The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute commissionable the Prospective Investigation of Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis (PIOPED) ที่ได้ทำการ revisedใหม่ เรียกว่า modified หรือ revised PIOPED criteria มาช่วยในการแปลผล lung scan โดยมีหลักการแปลผลเพื่อวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism ตามตารางที่ 1 ในปัจจุบันหลายสถาบันนิยมใช้ criteria ของ The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute commissionable the Prospective Investigation of Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis (PIOPED) ที่ได้ทำการ revisedใหม่ เรียกว่า modified หรือ revised PIOPED criteria มาช่วยในการแปลผล lung scan โดยมีหลักการแปลผลเพื่อวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism ตามตารางที่ 1 |
| ตารางที่ 1 MODIFIED PIOPED CRITERIA FOR COMBINED V/Q SCAN INTERPRETATION |
| HIGH PROBABILITY : > 80% |
| Two or more large mismatched segmental defects |
 without a radiographic abnormality (or the perfusion defect is substantially larger than the radiographic abnormality) without a radiographic abnormality (or the perfusion defect is substantially larger than the radiographic abnormality) |
| Any combination of mismatched defects |
 equivalent to the above (two moderate defects one large defect) equivalent to the above (two moderate defects one large defect) |
| INTERMEDIATE PROBABILITY > 20% - 80% |
| One moderate mismatched segmental defect with a normal radiograph |
| One large and on moderate mismatched |
 segmental defect with a normal radiograph segmental defect with a normal radiograph |
| Difficult to categorize as high or low probability Not meeting the stated criteria for high or low probability |
| LOW PROBABILITY : <20% |
| No segmental perfusion defects (e.g., small pleural |
 effusion with blunting of costophrenic angle. effusion with blunting of costophrenic angle. |
 cardiomegaly, elevated diaphragm, or cardiomegaly, elevated diaphragm, or |
 enlargement of the aorta, hila, or mediastinum) enlargement of the aorta, hila, or mediastinum) |
| Any perfusion defect substantially smaller than a corresponding radiographic abnormality |
| Matched ventilation and perfusion defects with a normal chest radiograph |
| Small subsegmental perfusion defects |
| NORMAL |
| No perfusion defects |
|
| หมายเหตุ : |
segmental defect หมายถึง defect ที่ occupy มากกว่า 75% ของ segment ของปอด |
| : |
moderate defect หมายถึง defect ที่ occupy อยู่ระหว่าง 25% - 75% ของ segment ของปอด |
| : |
small or subsegmental defect หมายถึง defect ที่ occupy น้อยกว่า 25% ของ segment ของปอด |
| : |
nonsegmental defect หมายถึง defect ที่ไม่เข้ากับรูปร่างของ segment ของปอด ซึ่งอาจพบว่ามีสาเหตุจาก tumor , pneumonia, hemorrhage,
|
|
| High Probability : |
จะบ่งชี้ถึงภาวะ pulmonary embolism โดยมี specificity ประมาณ 97% และมี positive predictive value ประมาณ 88% |
| Low Probability :- |
จะมี negative predictive value ประมาณ 84% |
|
| Intermediate Probability :- |
ไม่ได้ช่วยในการวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism แต่ถ้าผู้ป่วยมีอาการทางคลินิกชัดเจนควรทำ pulmonary arteriography หรือการตรวจอย่างอื่นเพื่อช่วยในการวินิจฉัยต่อไป |
|
| การตรวจทางรังสีวิทยาอื่นๆ ที่ช่วยวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism ได้แก่ |
 1. Pulmonary arteriography 1. Pulmonary arteriography
 ถือเป็น gold standard ในการวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism โดยลักษณะที่เป็น pathognomonic คือ มี intraluminal filling defect แต่การทำ pulmahary arteriography จัดเป็นวิธีที่ invasive และพบภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่อันตรายได้ ภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่อาจเกิดขึ้น เช่น cardiac perforation, contrast reaction, arrhythmia เป็นต้น ถือเป็น gold standard ในการวินิจฉัยภาวะ pulmonary embolism โดยลักษณะที่เป็น pathognomonic คือ มี intraluminal filling defect แต่การทำ pulmahary arteriography จัดเป็นวิธีที่ invasive และพบภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่อันตรายได้ ภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่อาจเกิดขึ้น เช่น cardiac perforation, contrast reaction, arrhythmia เป็นต้น |
 2. Spiral Computed Tomography (CT angiography) 2. Spiral Computed Tomography (CT angiography)
 ใช้แสดง large vessel emboli ได้ดี แต่ความถูกต้องแม่นยำลดลงในกรณีที่เป็น multiple small emboli ใช้แสดง large vessel emboli ได้ดี แต่ความถูกต้องแม่นยำลดลงในกรณีที่เป็น multiple small emboli |
 การรักษาภาวะ pulmonary embolism ที่สำคัญคือ การให้ anticoagulant โดย anticoagulant ได้แก่ heparin, low molecular weight heparin และ warfarin โดยแนะนำให้ therapeutic anticoagulation เป็นเวลา 4 ถึง 6 เดือน เพื่อป้องกันภาวะ recurrent pulmonary embolism การรักษาภาวะ pulmonary embolism ที่สำคัญคือ การให้ anticoagulant โดย anticoagulant ได้แก่ heparin, low molecular weight heparin และ warfarin โดยแนะนำให้ therapeutic anticoagulation เป็นเวลา 4 ถึง 6 เดือน เพื่อป้องกันภาวะ recurrent pulmonary embolism |
 ในการทำ lung scan เพื่อติดตามการรักษาภาวะ pulmonary embolism พบว่าภายหลังการรักษา บริเวณที่มี perfusion defects จะสามารถกลับเป็นปกติได้โดยเฉลี่ยภายใน 2 สัปดาห์แรก แล้วค่อยๆ ดีขึ้น ภายในเวลา 3 เดือน ทั้งนี้ขึ้นกับขนาดของ defect และอายุของผู้ป่วยด้วย ในการทำ lung scan เพื่อติดตามการรักษาภาวะ pulmonary embolism พบว่าภายหลังการรักษา บริเวณที่มี perfusion defects จะสามารถกลับเป็นปกติได้โดยเฉลี่ยภายใน 2 สัปดาห์แรก แล้วค่อยๆ ดีขึ้น ภายในเวลา 3 เดือน ทั้งนี้ขึ้นกับขนาดของ defect และอายุของผู้ป่วยด้วย |